RHV / oVirt / OLVM Monitoring
Follow installation procedure for your operating system platform
Install LPAR2RRD server (all under lpar2rrd user)
-
Download the latest LPAR2RRD server
Upgrade your already running LPAR2RRD instance.
- Install it:
# su - lpar2rrd $ tar xvf lpar2rrd-7.XX.tar $ cd lpar2rrd-7.XX $ ./install.sh $ cd /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd
- Make sure all Perl modules are in place
cd /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd . etc/lpar2rrd.cfg; $PERL bin/perl_modules_check.pl
If there is missing "LWP::Protocol::https" then check this docu to fix it
- Enable Apache authorisation
su - lpar2rrd umask 022 cd /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd cp html/.htaccess www cp html/.htaccess lpar2rrd-cgi
- Schedule to run it from lpar2rrd crontab (it might already exist there)
Add if it does not exist as above$ crontab -l | grep load.sh $
$ crontab -e # LPAR2RRD UI 0,30 * * * * /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd/load.sh > /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd/load.out 2>&1
Assure there is just one such entry in crontab.
- You might need to add lpar2rrd user into /etc/cron.allow (Linux) or /var/adm/cron/cron.allow (AIX) if 'crontab -e' command fails
Allow it for lpar2rrd user as root user.# echo "lpar2rrd" >> /etc/cron.allow
- Assure you have a cron jobs for oVirt in place (upgrade script might do it automatically)
Skip it on the Virtual Appliance, it is already there.Add it if it does not exist like above$ crontab -l | grep "load_ovirt.sh" $
$ crontab -e # oVirt/RHV support 0,20,40 * * * * /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd/load_ovirt.sh > /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd/load_ovirt.out 2>&1
-
Initial start from cmd line:
$ cd /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd $ ./load.sh
- Go to the web UI: http://<your web server>/lpar2rrd/
Use Ctrl-F5 to refresh the web browser cache.
Troubleshooting
-
If you have any problems with the UI then check:
(note that the path to Apache logs might be different, search apache logs in /var)tail /var/log/httpd/error_log # Apache error log tail /var/log/httpd/access_log # Apache access log tail /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-realt-error.log # STOR2RRD CGI-BIN log tail /var/tmp/systemd-private*/tmp/lpar2rrd-realt-error.log # STOR2RRD CGI-BIN log when Linux has enabled private temp
- Test of CGI-BIN setup
umask 022 cd /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd/ cp bin/test-healthcheck-cgi.sh lpar2rrd-cgi/
go to the web browser: http://<your web server>/lpar2rrd/test.html
You should see your Apache, LPAR2RRD, and Operating System variables, if not, then check Apache logs for connected errors
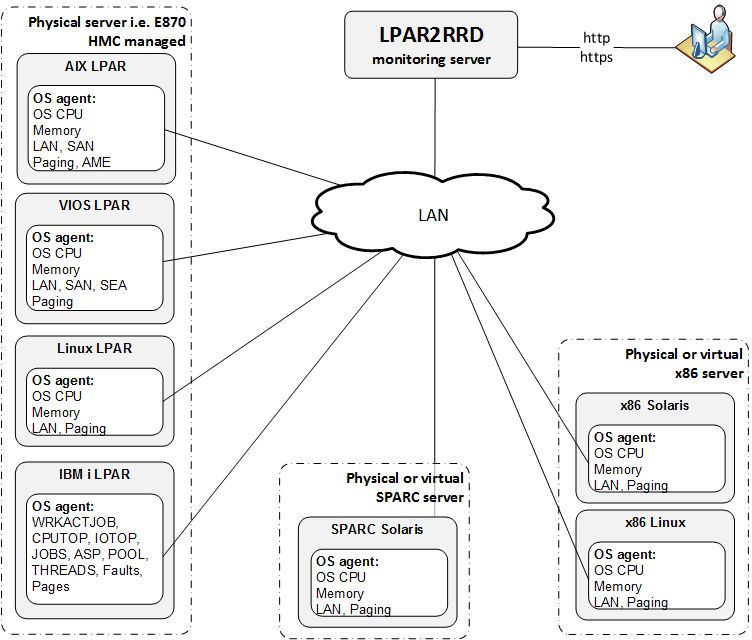
OS agent is add-on feature for monitoring from operating system level.
It is monitoring CPU, memory utilization, paging, LAN and SAN traffic on all adapters.
It requires the OS agent deployment to every monitored VM or KVM host.
The agent is written in Perl and calls basic OS commands to obtain required statistics like vmstat, iostat.
 |
Additional information about the OS agent:
- OS agent description
- OS agent release notes and download
- Features supported by the OS agent.
Prerequisites
- Perl
- Opened TCP communication between each VM and LPAR2RRD server on port 8162.
Connections are initiated from VM side. - Additional disk space on LPAR2RRD server (about 40MB per each monitored VM)
-
Create preferable dedicated user lpar2rrd on each VM with minimum rights
# useradd -c "LPAR2RRD agent user" -m lpar2rrd
OS agent installation (client)
-
Get the latest OS agent from download page
- Linux installation under root
# rpm -Uvh lpar2rrd-agent-6.00-0.noarch.rpm # rpm -qa|grep lpar2rrd-agent lpar2rrd-agent-6.00-0
- Linux Debian
# apt-get install lpar2rrd-agent_6.00-0_all.deb lpar2rrd-agent-6.00-0
- Solaris x86 installation under root:
# gunzip lpar2rrd-agent-6.00-0.solaris-i86pc.tar.gz # tar xf lpar2rrd-agent-6.00-0.solaris-i86pc.tar # pkgadd -d . The following packages are available: 1 lpar2rrd-agent LPAR2RRD OS agent 6.00 (i86pc) 6.00 ...Solaris upgrade under root:# pkgrm lpar2rrd-agent # pkgadd -d .
- Schedule its run every minute from the crontab on every VM.
This line must be placed into lpar2rrd crontab:# su - lpar2rrd $ crontab -e * * * * * /usr/bin/perl /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl <LPAR2RRD-SERVER> > /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent.out 2>&1
Replace <LPAR2RRD-SERVER> by hostname of your LPAR2RRD server.
-
You might need to add lpar2rrd user into /var/adm/cron/cron.allow under root user if above "crontab -e" fails.
# echo "lpar2rrd" >> /var/adm/cron/cron.allow
LPAR2RRD server (daemon)
-
Edit etc/lpar2rrd.cfg and set following (if it is not already set):
$ vi /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd/etc/lpar2rrd.cfg LPAR2RRD_AGENT_DAEMON=1
-
The daemon is started when load.sh starts
$ ./load.sh Starting LPAR2RRD daemon on port:8162 ...
- Assure it is running and listening on port 8162:
$ ps -ef|grep lpar2rrd-daemon lpar2rrd 10617010 1 0 Mar 16 - 0:00 /usr/bin/perl -w /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd/bin/lpar2rrd-daemon.pl $ netstat -an| grep 8162 tcp4 0 0 *.8162 *.* LISTEN
- OS agent data graphs will appear in the UI, use Ctrl-F5 to refresh your web browser
Troubleshooting
-
Client (agent) side:
-
Test if communication through the LAN is allowed.
$ telnet <LPAR2RRD-SERVER> 8162 Connected to 192.168.1.1 . Escape character is '^]'.
This is ok, exit either Ctrl-C or ^].
-
Check following agent files:
data store: /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent-*.txt
error log: /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent-*.err
output log: /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent.out
-
run the agent from cmd line:
$ /usr/bin/perl /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl -d <LPAR2RRD-SERVER> ... Agent send : yes : forced by -d Agent send slp: sending wait: 4 OS agent working for server: <LPAR2RRD-SERVER> store file for sending is /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent-<LPAR2RRD-SERVER>-lpar2rrd.txt
It means that data has been sent to the server, all is fine
Here is example when the agent is not able to sent data :$ /usr/bin/perl /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl -d <LPAR2RRD-SERVER> ... Agent send : yes : forced by -d Agent send slp: sending wait: 1 OS agent working for server: <LPAR2RRD-SERVER> store file for sending is /var/tmp/lpar2rrd-agent-<LPAR2RRD-SERVER>-lpar2rrd.txt Agent timed out after : 50 seconds /opt/lpar2rrd-agent/lpar2rrd-agent.pl:265
It means that the agent could not contact the server.
Check communication, port, above telnet example, DNS resolution of the server etc.
-
Test if communication through the LAN is allowed.
-
Server side:
- test if the daemon on LPAR2RRD server is running, and checking the logs
$ ps -ef|grep lpar2rrd-daemon lpar2rrd 10617010 1 0 Mar 16 - 0:00 /usr/bin/perl -w /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd/bin/lpar2rrd-daemon.pl $ cd /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd $ tail logs/error.log-daemon $ tail logs/daemon.out new server has been found and registered: Linux (lpar=linuxhost01) mkdir : /lpar2rrd/data/Linux/no_hmc/linuxhost01/
It means that new OS agent has been registered from linuxhost01 (Linux stand-alone example)
-
Test if OS agent data is being stored on the LPAR2RRD server and have actual timestamp:
$ cd /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd $ ls -l data/<server name>/*/<VM name>/*mmm -rw-r--r-- 2 lpar2rrd staff 7193736 Mar 17 16:16 data/<server name>/no_hmc/<VM name>/cpu.mmm -rw-r--r-- 2 lpar2rrd staff 7193736 Mar 17 16:16 data/<server name>/no_hmc/<VM name>/lan-en1.mmm -rw-r--r-- 2 lpar2rrd staff 10790264 Mar 17 16:16 data/<server name>/no_hmc/<VM name>/mem.mmm -rw-r--r-- 2 lpar2rrd staff 7193736 Mar 17 16:16 data/<server name>/no_hmc/<VM name>/pgs.mmm -rw-r--r-- 2 lpar2rrd staff 7193736 Mar 17 16:16 data/<server name>/no_hmc/<VM name>/san-vscsi0.mmm -rw-r--r-- 2 lpar2rrd staff 3597208 Mar 17 16:16 data/<server name>/no_hmc/<VM name>/san_resp-vscsi0.mmm $ find data -name mem.mmm -exec ls -l {} \; ...
- test if the daemon on LPAR2RRD server is running, and checking the logs
-
In case of a problem check our forum or contact us via support@lpar2rrd.com.
We would need this data for start of troubleshooting.
Notes
-
You will not need to upgrade LPAR2RRD agents regularly with each LPAR2RRD upgrade.
Read release notes if that is necessary.
Check OS agent upgrade steps.
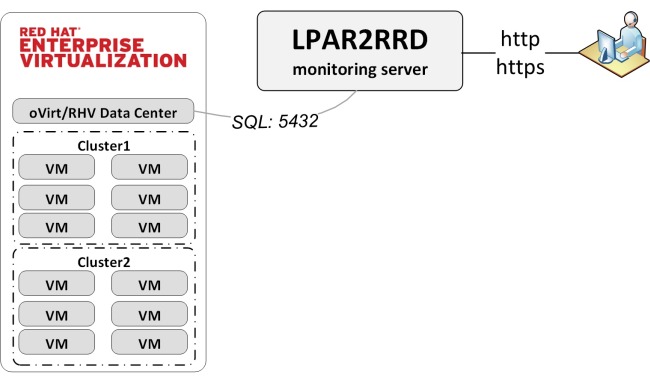 |
Implementation is agent less.
Data source is ovirt_engine_history database which is part of Data Warehouse on oVirt/RHV Virtualization Manager.
Tool accesses the ovirt_engine_history database remotely via its SQL API.
ovirt_engine_history database contains only historical performance data. There is only the admin account which we use.
OS Prerequisites
-
Open network connection to the RedHat Virtualization Manager on port 5432
$ perl /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd/bin/conntest.pl <Virtualization Manager/IP> 5432 Connection to "<Virtualization Manager hostname/IP>" on port "80" is ok
-
Make sure you have installed perl modules: perl-DBI and perl-DBD-Pg on LPAR2RRD server
Install them if they are missing under root user
$ rpm -q perl-DBI perl-DBD-Pg perl-DBI-1.627-4.el7.x86_64 perl-DBD-Pg-2.19.3-4.el7.x86_64
- Linux RedHat, CentOS
# yum install perl-DBD-Pg
- Linux Debian, Ubuntu
# apt-get install libdbd-pg-perl
-
AIX
- yum installation
Download perl-DBI-1.623-1 and perl-DBD-Pg-3.7.4
# yum install postgresql-libs # rpm -i perl-DBI-1.623-1.aix5.1.ppc.rpm # rpm -i perl-DBD-Pg-3.7-4.ppc.rpm
- manual rpm installation
- yum installation
- Linux RedHat, CentOS
Database access
-
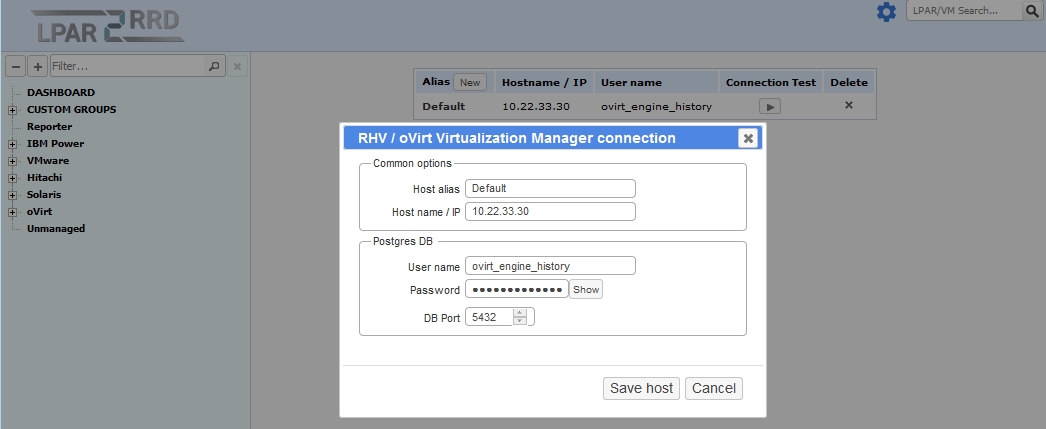
Each Virtualization Manager has its own randomly generated password for ovirt_engine_history database.
To get the database password, you have to connect to your RHV / oVirt engine via SSH and run this command:
# grep DWH_DB_PASSWORD /etc/ovirt-engine-dwh/ovirt-engine-dwhd.conf.d/10-setup-database.conf
# grep DWH_DB_USER /etc/ovirt-engine-dwh/ovirt-engine-dwhd.conf.d/10-setup-database.conf ovirt_engine_history
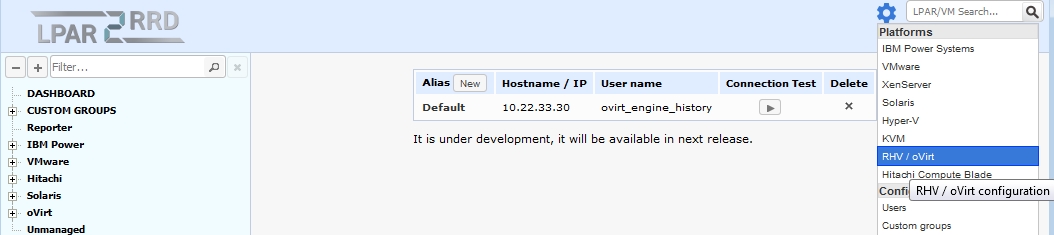
Attach oVirt / RHV
-
All is configured from the UI.
- Assure you have a cron jobs for oVirt in place (upgrade script might do it automatically)
Skip it on the Virtual Appliance, it is already there.Add it if it does not exist like above$ crontab -l | grep "load_ovirt.sh" $
$ crontab -e # oVirt/RHV support 0,20,40 * * * * /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd/load_ovirt.sh > /home/lpar2rrd/lpar2rrd/load_ovirt.out 2>&1
- Wait 30 minutes and then go to the web UI: http://<your web server>/lpar2rrd/
Use Ctrl-F5 to refresh the web browser cache.